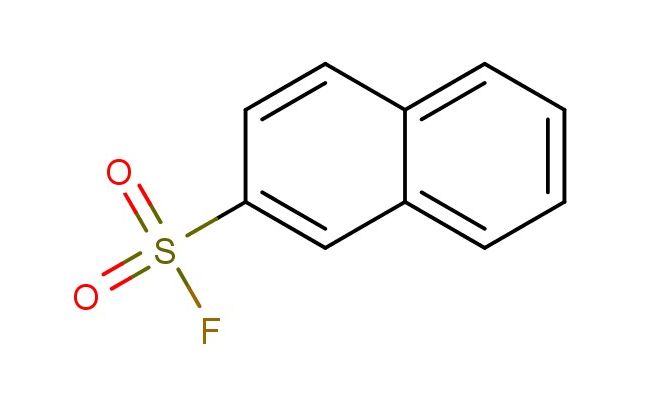
naphthalene-2-sulfonyl fluoride
$350.00
CAS No.: 325-12-2
Catalog No.: TQP2735
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H7FO2S
MW: 210.229
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C1=C(C=CC2=CC=CC=C12)S(=O)(=O)F
Catalog No.: TQP2735
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H7FO2S
MW: 210.229
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C1=C(C=CC2=CC=CC=C12)S(=O)(=O)F
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS NO.: 325-12-2; naphthalene-2-sulfonyl fluoride. PROPERTIES: naphthalene-2-sulfonyl fluoride appears as white crystalline powder that is odorless when pure. Its molecular formula is C10H7FNO2S, with a molecular weight of 230.23 g/mol. The compound has a melting point between 68-72 C and exhibits low water solubility but dissolves in acetone and ethyl acetate. Proper storage requires temperatures of 2-8 degree Celsius in glass containers lined with inert material to prevent reaction with container surfaces. When handling, extreme caution is necessary as it is a potent alkylating agent that causes severe skin burns and eye damage. The substance is highly reactive toward nucleophiles and should be managed in well-ventilated areas away from heat and ignition sources. It is stable under anhydrous conditions but hydrolyzes in aqueous environments to form naphthalenesulfonic acid and hydrofluoric acid, which are both corrosive. APPLICATIONS: naphthalene-2-sulfonyl fluoride is primarily utilized as a serine protease inhibitor in biochemical research. The fluorosulfonyl group covalently modifies the active site serine residue, providing irreversible inhibition of enzyme activity. This makes the compound invaluable in studying protease function and inhibition mechanisms in cellular signaling pathways. In protein purification, the compound is used to stabilize target proteins by inhibiting proteolytic degradation during isolation procedures. The naphthalene group provides hydrophobic character that enhances membrane permeability when incorporated into drug candidates, facilitating the delivery of sulfonyl fluoride-containing compounds to intracellular targets. In chemical biology, derivatives of this compound are employed as activity-based probes to profile protease expression levels in complex biological samples. Additionally, the compound serves as a building block for synthesizing fluorescently labeled inhibitors used in high-throughput screening assays to identify protease inhibitors with potential therapeutic applications. The structural rigidity of the naphthalene scaffold enhances the binding affinity of resulting inhibitors, making them suitable for developing targeted cancer therapies where dysregulated proteolysis contributes to disease progression.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review