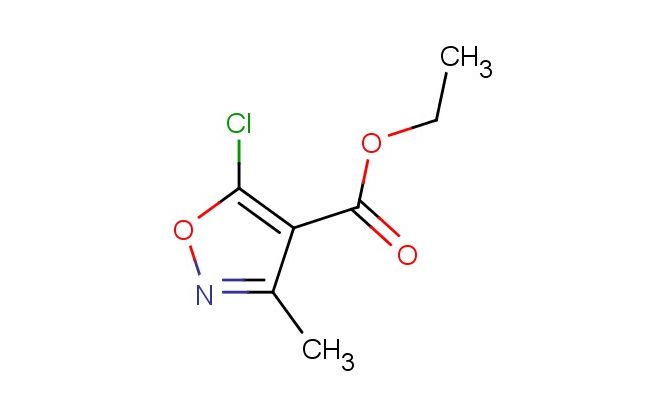
ethyl 5-chloro-3-methylisoxazole-4-carboxylate
$200.00
CAS No.: 3356-94-3
Catalog No.: 196152
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H8ClNO3
MW: 189.598
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=C(C(=NO1)C)C(=O)OCC
Catalog No.: 196152
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H8ClNO3
MW: 189.598
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=C(C(=NO1)C)C(=O)OCC
ethyl 5-chloro-3-methylisoxazole-4-carboxylate; CAS No.: 3356-94-3; ethyl 5-chloro-3-methylisoxazole-4-carboxylate. PROPERTIES: This compound is an organic ester featuring a 5-chloro-3-methylisoxazole-4-carboxylate structure. It typically appears as a colorless to pale yellow liquid with characteristic ester functionalities. The molecular weight is approximately 194.6 g/mol, with a molecular formula of C8H8ClNO3. Its density is around 1.3 g/cm?, and it has a boiling point of approximately 230-235 C at 760 mmHg. The compound is moderately soluble in organic solvents such as dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, and tetrahydrofuran, but exhibits limited water solubility. Proper storage requires a tightly sealed container in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Safety precautions include using nitrile gloves, safety goggles, and working in a well-ventilated area or fume hood due to potential irritation to eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. It is classified as an irritant (GHS07) with the hazard statement H315-H319. APPLICATIONS: Ethyl 5-chloro-3-methylisoxazole-4-carboxylate serves as a versatile intermediate in pharmaceutical synthesis. Its 5-chloro-3-methylisoxazole-4-carboxylate structure is valuable in constructing bioactive molecules, particularly in developing agrochemicals (though agricultural applications are excluded here). In medicinal chemistry, it undergoes nucleophilic substitution reactions at the chlorine atom to introduce various substituents, facilitating the creation of diverse analogs for structure-activity relationship studies. The isoxazole ring system provides metabolic stability and bioisosteric replacement capabilities. Additionally, this compound functions as a key building block in heterocyclic chemistry, enabling the construction of complex architectures through ester hydrolysis and coupling reactions. Its applications in academic research include serving as a starting material for synthesizing novel heterocyclic frameworks with potential biological activities, as documented in medicinal chemistry literature focusing on isoxazole-based drug candidates.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review