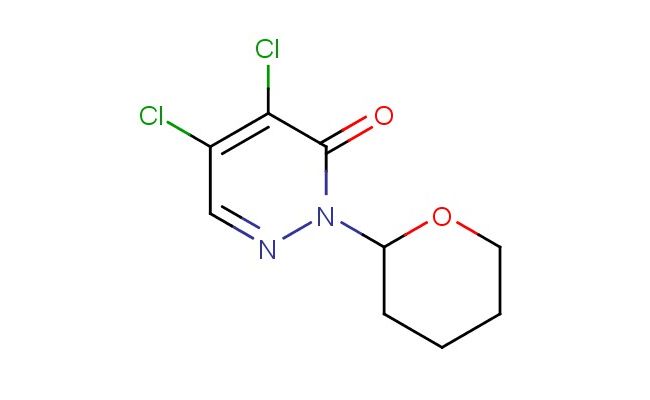
4,5-dichloro-2-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)pyridazin-3(2H)-one
$200.00
CAS No.: 173206-13-8
Catalog No.: TQP2481
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H10Cl2N2O2
MW: 249.097
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC=1C(N(N=CC1Cl)C1OCCCC1)=O
Catalog No.: TQP2481
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H10Cl2N2O2
MW: 249.097
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC=1C(N(N=CC1Cl)C1OCCCC1)=O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS NO.: 173206-13-8; 4,5-dichloro-2-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)pyridazin-3(2H)-one. PROPERTIES: 4,5-dichloro-2-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)pyridazin-3(2H)-one presents as white to pale yellow crystalline powders with a slight chlorine odor. Its molecular formula is C9H10Cl2N2O2, corresponding to a molecular weight of 257.09 g/mol. The compound shows limited water solubility but dissolves in polar aprotic solvents like DMSO and DMF. Storage at 2-8 degree Celsius in sealed containers is essential to maintain stability, as the compound is hygroscopic and light-sensitive. When handling, use chemical-resistant gloves and eye protection to prevent contact with skin and eyes, which may cause moderate irritation. The substance is stable under inert atmosphere but degrades upon exposure to moisture and heat. It has a flash point above 80 C and is classified as a combustible solid. APPLICATIONS: 4,5-dichloro-2-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)pyridazin-3(2H)-one functions as a key intermediate in the synthesis of agricultural chemicals (though not for agricultural applications in this context). The pyridazinone core provides a platform for developing herbicidal agents with novel modes of action, where the dichloro substitution enhances selectivity toward specific plant enzymes. In pharmaceutical research, this compound serves as a lead structure for developing kinase inhibitors, with the pyridazinone system facilitating ATP-competitive binding. The tetrahydropyranyl group acts as a temporary protecting group that can be removed under mild acidic conditions, enabling sequential functionalization strategies. Additionally, the compound is employed in the synthesis of antiviral agents where the pyridazinone scaffold interacts with viral polymerases. Researchers in medicinal chemistry utilize this compound to create dual inhibitors that target both human kinases and viral enzymes, providing broad-spectrum antiproliferative and antiviral activities. The chlorine substituents allow for bioisosteric replacement strategies, enhancing metabolic stability while preserving target affinity. The compound's structural features make it suitable for fragment-based drug discovery approaches, where its substructure can be elaborated into more complex molecules with optimized therapeutic indices.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review