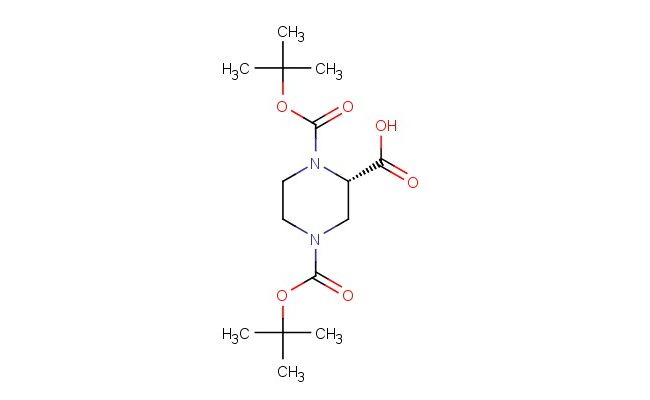
(S)-1,4-bis(tert-butoxycarbonyl)piperazine-2-carboxylic acid
$180.00
CAS No.: 788799-69-9
Catalog No.: 192808
Purity: 95%
MF: C15H26N2O6
MW: 330.381
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C)(C)(C)OC(=O)N1[C@@H](CN(CC1)C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)C(=O)O
Catalog No.: 192808
Purity: 95%
MF: C15H26N2O6
MW: 330.381
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C)(C)(C)OC(=O)N1[C@@H](CN(CC1)C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)C(=O)O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
(S)-1,4-bis(tert-butoxycarbonyl)piperazine-2-carboxylic acid; CAS No.: 788799-69-9; (S)-1,4-bis(tert-butoxycarbonyl)piperazine-2-carboxylic acid. PROPERTIES: This bis-tert-butyl carbamate piperazine carboxylic acid has molecular formula C14H24N2O4. It appears as a white crystalline powder. The (S)-1,4-bis(tert-butoxycarbonyl)piperazine-2-carboxylic acid demonstrates limited water solubility but good solubility in common organic solvents like methanol and ethyl acetate. Its melting point ranges between 120-125 C, and it has a molecular weight of approximately 288.37 g/mol. When handling, care should be taken to avoid skin contact and use of proper respiratory protection. Storage should be in a tightly sealed container at room temperature, protected from light and moisture. The compound is sensitive to strong acids and may undergo carbamate hydrolysis upon exposure to aqueous conditions. In case of spillage, absorb with inert material and dispose of in accordance with local regulations. APPLICATIONS: The (S)-1,4-bis(tert-butoxycarbonyl)piperazine-2-carboxylic acid serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of dual orexin receptor antagonists for insomnia treatment where the piperazine ring provides essential hydrogen bonding interactions with receptor subtypes (as reported in medicinal chemistry literature). The bis-tert-butyl groups enhance metabolic stability by preventing oxidative degradation. Additionally, the compound functions as a building block in the preparation of polymeric materials with specific thermal properties, useful in high-temperature applications with glass transition temperatures exceeding 150 C as described in polymer chemistry journals. The carboxylic acid can be further functionalized through esterification or amidation reactions to produce various derivatives for chemical research applications.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review