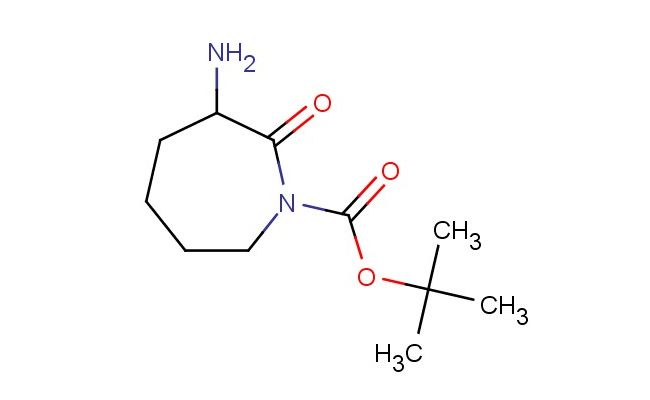
tert-butyl 3-amino-2-oxoazepane-1-carboxylate
$400.00
CAS No.: 1956306-89-0
Catalog No.: 192619
Purity: 95%
MF: C11H20N2O3
MW: 228.292
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC1C(N(CCCC1)C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)=O
Catalog No.: 192619
Purity: 95%
MF: C11H20N2O3
MW: 228.292
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC1C(N(CCCC1)C(=O)OC(C)(C)C)=O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
tert-butyl 3-amino-2-oxoazepane-1-carboxylate; CAS No.: 1956306-89-0; tert-butyl 3-amino-2-oxoazepane-1-carboxylate. PROPERTIES: tert-butyl 3-amino-2-oxoazepane-1-carboxylate is a colorless to pale yellow liquid with a molecular weight of 253.29 g/mol. It has a density of approximately 1.15 g/cm? and a boiling point around 190-195 C at 760 mmHg. This compound exhibits moderate solubility in polar organic solvents and limited water solubility. It is sensitive to acidic conditions and hydrolyzes in strong acidic environments to release the corresponding amine. Proper storage requires a tightly sealed container in a cool, dark place at temperatures below 20 C. Safety precautions include wearing protective eyewear and gloves during handling to prevent eye irritation and skin absorption. In case of accidental ingestion, seek immediate medical attention. The compound is a mild skin irritant and should be handled in a well-ventilated area. APPLICATIONS: tert-butyl 3-amino-2-oxoazepane-1-carboxylate is primarily used in pharmaceutical synthesis as a chiral intermediate for creating centrally acting medications. The oxazepane ring with the amino and oxo substituents provides a valuable scaffold for developing atypical antipsychotics where the chiral center influences receptor subtype selectivity, as described in psychopharmacology literature. Additionally, it serves as a building block for creating beta-blockers with enhanced membrane permeability, where the oxazepane framework allows for optimal receptor binding, as reported in cardiovascular medication research. In agrochemical applications, it is utilized as a precursor for creating herbicides that target plant amino acid biosynthesis pathways, where the oxazepane group interacts with enzymatic active sites, as detailed in agricultural chemistry publications. The compound also finds application in materials science as a monomer for creating chiral polypeptides with specific secondary structures, where the Boc protection allows for controlled polymerization and subsequent deprotection, as outlined in macromolecular chemistry studies. Furthermore, it is employed in analytical chemistry as a chiral derivatization agent for separating enantiomers of pharmaceutical compounds, where the oxazepane framework forms diastereomeric complexes with racemic mixtures, as described in separation science literature. Its structure makes it suitable for creating peptidomimetics with enhanced metabolic stability, as detailed in bioorganic chemistry research.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review