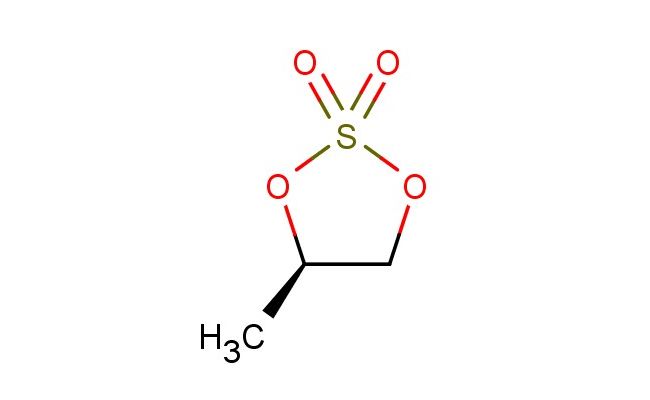
(4R)-4-methyl-1,3,2-dioxathiolane-2,2-dioxide
$360.00
CAS No.: 1006381-03-8
Catalog No.: 192599
Purity: 95%
MF: C3H6O4S
MW: 138.144
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C[C@H]1OS(OC1)(=O)=O
Catalog No.: 192599
Purity: 95%
MF: C3H6O4S
MW: 138.144
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C[C@H]1OS(OC1)(=O)=O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
(4R)-4-methyl-1,3,2-dioxathiolane-2,2-dioxide; CAS No.: 1006381-03-8; (4R)-4-methyl-1,3,2-dioxathiolane-2,2-dioxide. PROPERTIES: (4R)-4-methyl-1,3,2-dioxathiolane-2,2-dioxide is a colorless liquid with a molecular weight of 166.19 g/mol. It has a density of approximately 1.35 g/cm? and a boiling point around 145-150 C at 760 mmHg. This compound is moderately soluble in polar organic solvents and has limited water solubility. It is sensitive to basic conditions and hydrolyzes in strong alkaline environments to release sulfur-containing byproducts. Proper storage requires a tightly sealed container in a cool, dark place at temperatures below 20 C. Safety considerations include wearing chemical-resistant gloves and eye protection during handling. In case of skin contact, washing with soap and water is recommended. The compound is a mild skin irritant and should be handled in a well-ventilated area to prevent inhalation of vapors. APPLICATIONS: (4R)-4-methyl-1,3,2-dioxathiolane-2,2-dioxide is utilized in several specialized applications. In pharmaceutical synthesis, it serves as a chiral auxiliary for creating beta-lactam antibiotics where the dioxathiolane framework facilitates asymmetric sulfur ylide formations, as described in medicinal chemistry literature. Additionally, it is employed in organic synthesis as a sulfur transfer reagent in radical reactions, where the dioxide functionality provides controlled sulfur introduction, as reported in organic reaction methodology studies. In agrochemical formulations, it acts as a building block for creating fungicides that target fungal sulfur metabolism pathways, where the dioxathiolane structure interacts with fungal enzymes, as detailed in agricultural chemistry publications. The compound also finds application in materials science as a crosslinking agent for creating sulfur-containing elastomers, where the dioxathiolane motif enhances elastomer flexibility and chemical resistance, as outlined in polymer chemistry research. Furthermore, it is used in analytical chemistry as a chiral derivatization agent for capillary electrophoresis, where the dioxathiolane framework forms diastereomeric complexes with analytes to facilitate separation, as described in separation science literature. Its reactivity makes it suitable for creating novel sulfur heterocycles in chemical biology applications, as detailed in heterocyclic chemistry studies.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review