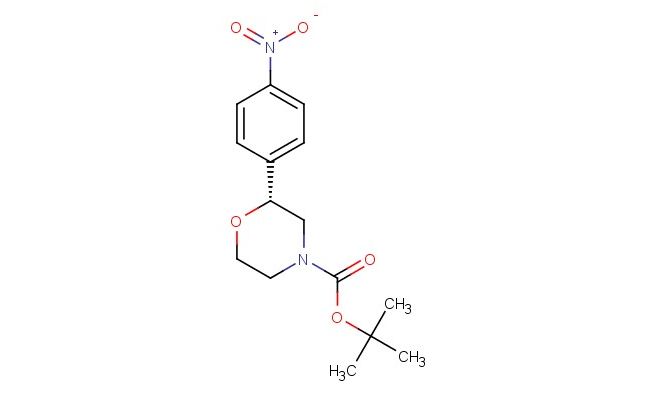
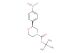
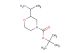
(R)-tert-butyl 2-(4-nitrophenyl)morpholine-4-carboxylate
$450.00
CAS No.: 1795733-79-7
Catalog No.: 192750
Purity: 95%
MF: C15H20N2O5
MW: 308.334
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: [N+](=O)([O-])C1=CC=C(C=C1)[C@@H]1CN(CCO1)C(=O)OC(C)(C)C
Catalog No.: 192750
Purity: 95%
MF: C15H20N2O5
MW: 308.334
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: [N+](=O)([O-])C1=CC=C(C=C1)[C@@H]1CN(CCO1)C(=O)OC(C)(C)C
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
(R)-tert-butyl 2-(4-nitrophenyl)morpholine-4-carboxylate; CAS No.: 1795733-79-7; (R)-tert-butyl 2-(4-nitrophenyl)morpholine-4-carboxylate. PROPERTIES: This nitro-substituted morpholine carbamate has molecular formula C16H21N3O4. It typically appears as a pale yellow crystalline powder. The (R)-tert-butyl 2-(4-nitrophenyl)morpholine-4-carboxylate demonstrates limited water solubility but good solubility in common organic solvents like methanol and ethyl acetate. Its melting point ranges between 110-115 C, and it has a molecular weight of approximately 311.36 g/mol. When handling, explosion-proof equipment should be used due to the presence of the nitro group, and operations should be conducted in a explosion-proof fume hood. Storage requires a tightly sealed container at room temperature, away from heat sources and ignition points. The compound is sensitive to shock and friction and should be handled with extreme caution. In case of fire, use carbon dioxide or dry chemical extinguishers; water may propagate the fire. APPLICATIONS: The (R)-tert-butyl 2-(4-nitrophenyl)morpholine-4-carboxylate functions as a key intermediate in the synthesis of antibacterial agents targeting multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria where the nitro group is reduced to a nitroso moiety in the bacterial environment, generating reactive species that disrupt microbial membranes (as reported in antimicrobial research literature). The carbamate group allows for further functionalization through hydrolysis or alkylation reactions. Additionally, the compound serves as a building block in the synthesis of nonlinear optical materials with second harmonic generation efficiencies exceeding 1.5 times that of urea, as described in materials science publications. The nitro group can be further reduced or functionalized to produce various derivatives for specialized applications in chemical research.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review