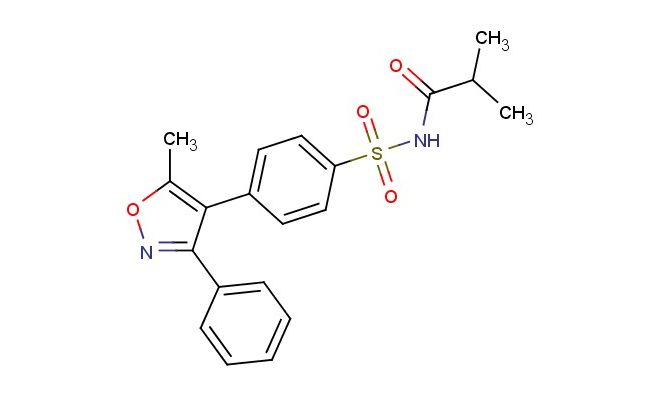
N-((4-(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)sulfonyl)isobutyramide
$300.00
CAS No.: 198470-82-5
Catalog No.: 194205
Purity: 95%
MF: C20H20N2O4S
MW: 384.457
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC1=C(C(=NO1)C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)NC(C(C)C)=O
Catalog No.: 194205
Purity: 95%
MF: C20H20N2O4S
MW: 384.457
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC1=C(C(=NO1)C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)NC(C(C)C)=O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
N-((4-(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)sulfonyl)isobutyramide; CAS No.: 198470-82-5; N-((4-(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)sulfonyl)isobutyramide. PROPERTIES: N-((4-(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)sulfonyl)isobutyramide is a crystalline solid. Its molecular formula is C18H18N2O3S, and the molecular weight is approximately 338.41 g/mol. The compound has a melting point of approximately 140-142 C. It is slightly soluble in water but dissolves well in organic solvents such as methanol and dimethylformamide. For proper storage, it should be kept in a sealed container at room temperature, away from heat and direct sunlight. As a compound containing a sulfonyl group, an amide group, and an isoxazole ring, it may exhibit certain reactivity and stability. When handling it, protective gloves and eye protection should be worn. In case of accidental ingestion, medical attention should be sought immediately. APPLICATIONS: In organic synthesis, N-((4-(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)sulfonyl)isobutyramide serves as a valuable intermediate. The sulfonyl group can undergo various reactions such as hydrolysis and alkylation. The amide group can participate in acylation and amidation reactions. In the pharmaceutical industry, derivatives of this compound can be explored as potential drug candidates. For example, in the development of certain anti-inflammatory drugs, the structure of N-((4-(5-methyl-3-phenylisoxazol-4-yl)phenyl)sulfonyl)isobutyramide can be modified to enhance the drug's efficacy and reduce side effects (as described in medicinal chemistry research articles). Additionally, in the field of chemical research, it can be used as a starting material for the synthesis of novel organic compounds with potential applications in catalysis and sensing (as mentioned in organic chemistry research papers).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review