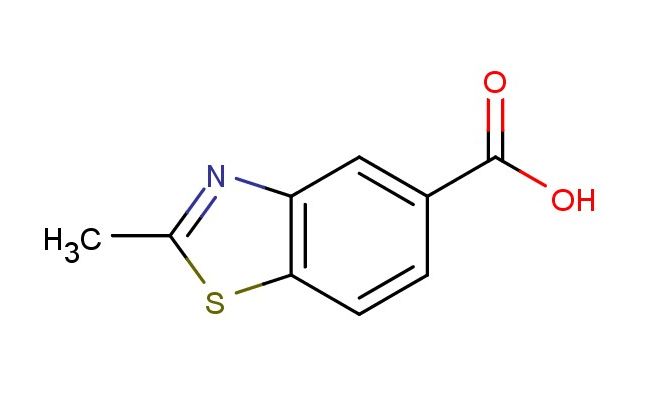
2-methylbenzo[d]thiazole-5-carboxylic acid
$300.00
CAS No.: 24851-69-2
Catalog No.: 192614
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H7NO2S
MW: 193.227
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC=1SC2=C(N1)C=C(C=C2)C(=O)O
Catalog No.: 192614
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H7NO2S
MW: 193.227
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: CC=1SC2=C(N1)C=C(C=C2)C(=O)O
2-methylbenzo[d]thiazole-5-carboxylic acid; CAS No.: 24851-69-2; 2-methylbenzo[d]thiazole-5-carboxylic acid. PROPERTIES: 2-methylbenzo[d]thiazole-5-carboxylic acid is a white crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 213.26 g/mol. It has a melting point between 200-205 C and is moderately soluble in polar solvents like methanol and water. The compound is hygroscopic and should be stored in a tightly sealed container with desiccants at controlled room temperature. Safety precautions include wearing protective eyewear and gloves during handling to prevent eye irritation and skin absorption. In case of accidental ingestion, seek immediate medical attention. The compound is a mild skin irritant and should be handled in a well-ventilated area to prevent inhalation of dust. APPLICATIONS: 2-methylbenzo[d]thiazole-5-carboxylic acid is predominantly used in pharmaceutical development as a building block for creating non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The methyl substituent on the benzo[d]thiazole ring enhances binding affinity to cyclooxygenase enzymes, as described in anti-inflammatory chemistry literature. Additionally, it serves as an intermediate for creating certain antipsychotic agents where the thiazole ring system interacts with dopamine receptors, as reported in psychopharmacology studies. In agrochemical applications, it is utilized as a precursor for creating herbicides that target plant enzyme systems involved in cell wall synthesis, where the benzo[d]thiazole structure disrupts specific biosynthetic pathways, as detailed in agricultural chemistry publications. The compound also finds application in materials science as a component of corrosion inhibitors for metals, where the nitrogen and sulfur atoms in the thiazole ring coordinate with metal surfaces, as outlined in materials chemistry studies. Furthermore, it is employed in analytical chemistry as a fluorescent probe for detecting certain metal ions, where the benzo[d]thiazole structure undergoes fluorescence changes upon metal binding, as described in analytical chemistry literature. Its structure makes it suitable for creating novel heterocycles through palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions in chemical biology applications, as detailed in heterocyclic chemistry research.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review



![methyl 2-methylbenzo[d]thiazole-5-carboxylate](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/192615_2.jpg)