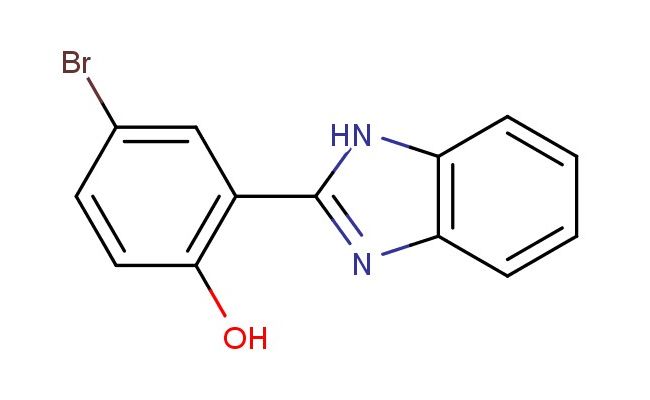
2-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-4-bromophenol
$350.00
CAS No.: 62871-28-7
Catalog No.: 196136
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H9BrN2O
MW: 289.132
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: N1C(=NC2=C1C=CC=C2)C2=C(C=CC(=C2)Br)O
Catalog No.: 196136
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H9BrN2O
MW: 289.132
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: N1C(=NC2=C1C=CC=C2)C2=C(C=CC(=C2)Br)O
2-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-4-bromophenol; CAS No.: 62871-28-7; 2-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-4-bromophenol. PROPERTIES: This crystalline solid has a molecular formula of C12H8BrN2O and a molecular weight of approximately 304.01 g/mol. It exhibits low water solubility but dissolves in DMSO and DMF. The compound is sensitive to light and should be stored in an amber glass bottle at 2-8 C. Thermogravimetric analysis shows decomposition starting at 230 C. Safety guidelines recommend using chemical-resistant gloves, face shields, and working in a fume hood. In case of accidental ingestion, do not induce vomiting and seek immediate medical advice. Avoid release to the environment as brominated phenolic compounds may persist and bioaccumulate. APPLICATIONS: 2-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-4-bromophenol serves as a valuable intermediate in pharmaceutical synthesis, particularly in the development of kinase inhibitors and GPCR modulators. Its bromophenol substituent enables Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions for creating diverse aryl patterns. The benzimidazole core provides a privileged scaffold for binding to various protein targets. Research groups employ it in the development of estrogen receptor degraders for breast cancer treatment. Academic institutions utilize it in teaching heterocyclic chemistry and Suzuki coupling methodologies. Industrial applications include its use as a building block in agrochemical development for novel fungicide candidates targeting enzyme inhibition. Recent publications in Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry highlight its role in fragment-based drug discovery approaches. Additionally, it finds utility in chemical biology as a warhead for covalent inhibitors targeting protein kinases. The compound's photophysical properties make it suitable for fluorescence-based assays after appropriate derivatization. Its ability to form hydrogen bonds enhances its utility in crystallographic studies of protein-ligand complexes.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review



![1-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-6-carboxylic acid](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/196133_2.jpg)
![2-chloro-4-fluoro-1H-benzo[d]imidazole](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/1/9/196138_2.jpg)