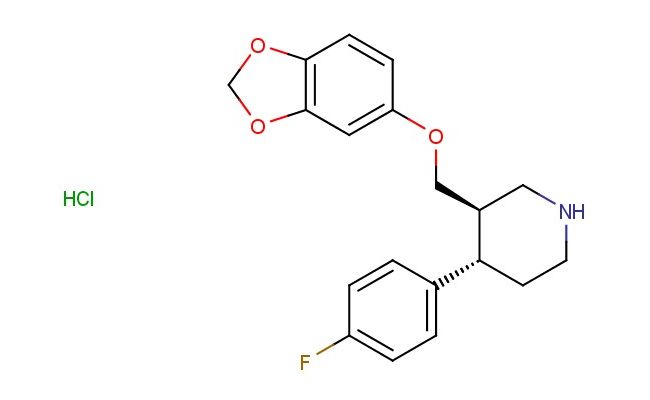
(3R,4S)-3-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yloxymethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperidine hydrochloride
$450.00
CAS No.: 130855-30-0
Catalog No.: WLZ0766
Purity: 95%
MF: C19H21ClFNO3
MW: 365.832
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: Cl.O1COC2=C1C=CC(=C2)OC[C@H]2CNCC[C@@H]2C2=CC=C(C=C2)F
Catalog No.: WLZ0766
Purity: 95%
MF: C19H21ClFNO3
MW: 365.832
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: Cl.O1COC2=C1C=CC(=C2)OC[C@H]2CNCC[C@@H]2C2=CC=C(C=C2)F
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS NO.: 130855-30-0; (3R,4S)-3-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yloxymethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperidine hydrochloride. PROPERTIES: (3R,4S)-3-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yloxymethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperidine hydrochloride appears as white to off-white crystalline powder with a slight ammoniacal odor. Its molecular formula is C19H20FNO4 HCl, corresponding to a molecular weight of 383.82 g/mol. The compound has a melting point between 128-132 C and is highly soluble in water, forming clear solutions. Proper storage requires maintenance at 2-8 degree Celsius in tightly sealed containers to prevent deliquescence. When handling, use powder-free gloves and avoid inhalation of dust particles which may cause respiratory irritation. The substance is stable under dry conditions but hydrolyzes in aqueous environments to release the free base and hydrochloric acid. It is classified as a mild irritant and should be managed in well-ventilated areas. The hydrochloride salt form enhances water solubility, facilitating formulation development for parenteral administration. The compound exhibits moderate hygroscopicity and should be protected from prolonged exposure to atmospheric moisture. The (3R,4S) configuration ensures proper spatial orientation of the substituents, which is critical for achieving optimal binding to target receptors. APPLICATIONS: (3R,4S)-3-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yloxymethyl)-4-(4-fluorophenyl)piperidine hydrochloride serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of serotonin receptor ligands and other central nervous system agents. The benzodioxole group provides aromatic character that enhances interactions with specific serotonin receptor subtypes. The fluorophenyl substituent contributes steric and electronic effects that modulate receptor binding affinity and selectivity. In medicinal chemistry, this compound is used to develop atypical antipsychotic agents where the piperidine scaffold facilitates interactions with both serotonin and dopamine receptors. The hydrochloride salt form ensures good bioavailability when administered orally, making it suitable for chronic treatment regimens. Researchers in neuropharmacology utilize this compound to create selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) with reduced side effect profiles. The compound functions as a building block for synthesizing tritiated ligands used in receptor binding assays to determine the affinity and selectivity of new drug candidates. Additionally, derivatives of this compound are employed in the development of anxiolytic agents where the piperidine core contributes to anxiolytic effects through interactions with specific GABA receptor subtypes. The compound's structural features make it suitable for use in fragment-based drug discovery approaches, where its substructure can be elaborated into more complex molecules with optimized therapeutic indices. It also serves as a starting material for synthesizing enantiomerically pure piperidines through reductive amination reactions, providing access to a wide range of chiral tertiary amines for pharmaceutical development. The benzodioxole group provides protection against oxidative metabolism, enhancing the metabolic stability of resulting compounds.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review



![5-bromo-2,2-dimethylbenzo[d][1,3]dioxole](https://www.chemshuttle.com/media/catalog/product/cache/31dbf0bffbfa69a5826a72cec9a446de/w/l/wlz2533_1.jpg)