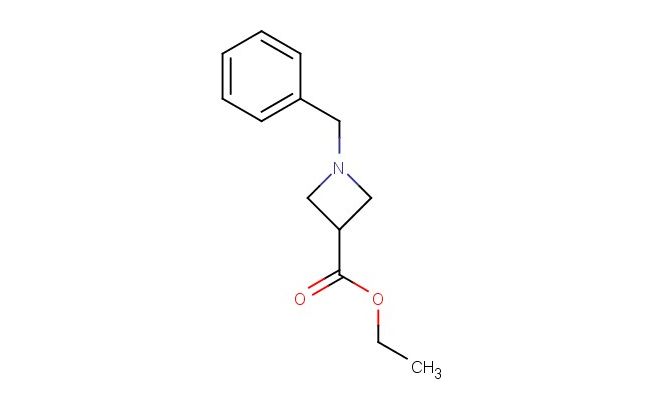
ethyl 1-benzylazetidine-3-carboxylate
$250.00
CAS No.: 103491-30-1
Catalog No.: 196131
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H17NO2
MW: 219.284
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C1=CC=CC=C1)N1CC(C1)C(=O)OCC
Catalog No.: 196131
Purity: 95%
MF: C13H17NO2
MW: 219.284
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(C1=CC=CC=C1)N1CC(C1)C(=O)OCC
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
ethyl 1-benzylazetidine-3-carboxylate; CAS No.: 103491-30-1; ethyl 1-benzylazetidine-3-carboxylate. PROPERTIES: This colorless oil has a molecular formula of C13H15NO3 and a molecular weight of approximately 233.26 g/mol. It exhibits moderate solubility in water and mixes well with common organic solvents. The compound is sensitive to basic conditions and should be stored in a tightly sealed container at 2-8 C. Thermogravimetric analysis shows decomposition starting at 180 C. Safety precautions include using chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and working in a well-ventilated area. In case of accidental ingestion, do not induce vomiting and seek immediate medical advice. Avoid release to the environment as it may be harmful to aquatic organisms. APPLICATIONS: Ethyl 1-benzylazetidine-3-carboxylate functions as a versatile intermediate in peptide synthesis and pharmaceutical development. Its azetidine core provides a four-membered nitrogen-containing ring useful in mimicking bioactive conformations. The benzyl group offers steric and electronic effects useful in modulating receptor binding. Research groups employ it in the development of GPCR-targeted small molecules for metabolic disease treatment. Academic institutions utilize it in teaching peptide synthesis and conformational analysis techniques. Industrial applications include its use as a building block in agrochemical development for novel insecticide candidates targeting neurotransmitter receptors. Recent studies in the Journal of Peptide Science highlight its application in developing constrained peptide analogs with improved metabolic stability. Additionally, it serves as a starting material for radiolabeled compounds used in receptor binding assays. The compound's ability to form hydrogen bonds makes it suitable for crystallographic studies of protein-ligand complexes. Its synthetic versatility enables rapid diversification through ester hydrolysis or benzyl group removal.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review