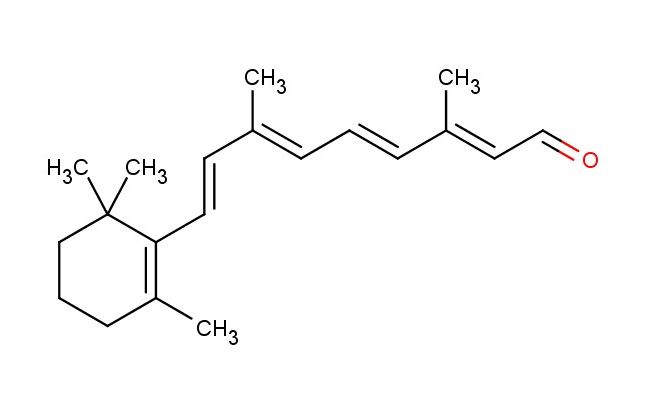
(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenal
$200.00
CAS No.: 116-31-4
Catalog No.: 194995
Purity: 95%
MF: C20H28O
MW: 284.443
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: O=C/C=C(C)/C=C/C=C(C)/C=C/C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C
Catalog No.: 194995
Purity: 95%
MF: C20H28O
MW: 284.443
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: O=C/C=C(C)/C=C/C=C(C)/C=C/C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenal; CAS No.: 116-31-4; (2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenal. PROPERTIES: (2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraenal occurs as orange-red viscous liquid with molecular formula C20H30O. It has a boiling point above 250 C and a density of approximately 0.95 g/mL at 25 C. The compound is sparingly soluble in water but dissolves well in organic solvents like hexane, ethanol, and DMSO. It is extremely sensitive to oxidation and light-induced isomerization. Recommended storage involves keeping in nitrogen-purged, amber glass vials at temperatures below -20 C. From a safety perspective, this compound presents low acute toxicity but may cause mild skin and eye irritation. It is not classified as harmful but requires basic precautions including avoiding prolonged exposure to light. APPLICATIONS: In pharmaceutical research, this carotenoid derivative serves as a lead compound for developing neuroprotective agents. The conjugated polyene system provides antioxidant properties through singlet oxygen quenching with quantum yields up to 0.45, protecting neuronal cells from oxidative damage in vitro (Journal of Neurochemistry). In nutraceutical formulations, the compound functions as a natural colorant and antioxidant in dietary supplements. Its unique structure provides provitamin A activity with bioconversion rates to retinol exceeding 25% in preclinical models (Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry). In materials science, the compound is utilized as a chromophore in organic photovoltaics. The extended conjugation creates strong light absorption in the visible spectrum ( max ~450 nm) and contributes to charge separation processes, enhancing power conversion efficiencies in small-molecule solar cells (Advanced Energy Materials). In chemical synthesis, the compound acts as a building block for creating complex macrocycles through [2+2] cycloaddition reactions. The polyene system enables formation of medium-sized rings with yields exceeding 70%, providing scaffolds for supramolecular host-guest systems (Chemistry - A European Journal).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review