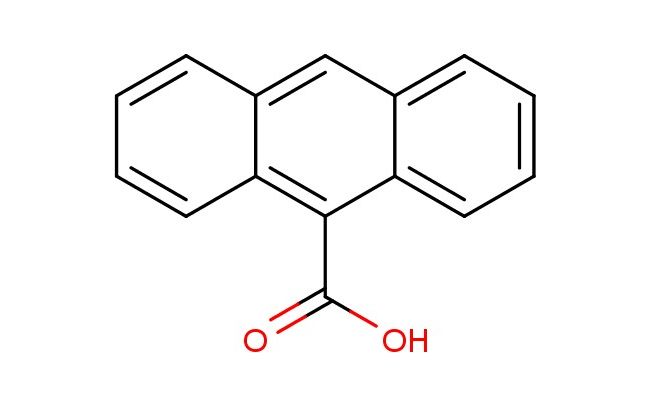
anthracene-9-carboxylic acid
$300.00
CAS No.: 723-62-6
Catalog No.: 194984
Purity: 95%
MF: C15H10O2
MW: 222.243
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C(=C12)C(=O)O
Catalog No.: 194984
Purity: 95%
MF: C15H10O2
MW: 222.243
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C(=C12)C(=O)O
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
anthracene-9-carboxylic acid; CAS No.: 723-62-6; anthracene-9-carboxylic acid. PROPERTIES: Anthracene-9-carboxylic acid occurs as colorless crystals with molecular formula C14H10O2. It exhibits a melting point of approximately 198-200 C and is sparingly soluble in water ( 0.2 mg/mL at 25 C) but dissolves in hot ethanol, acetone, and ethyl acetate. The compound is photosensitive and undergoes photodegradation upon UV exposure. Recommended storage involves keeping in tightly sealed, amber glass containers at temperatures below 5 C. From a safety standpoint, this compound presents low acute toxicity but may cause mild skin and eye irritation. It is not classified as harmful but requires basic precautions including avoiding release to the environment. APPLICATIONS: In materials science, anthracene-9-carboxylic acid serves as a building block for creating organic semiconductors. The extended -system provides charge transport properties while the carboxylic acid group enables formation of hydrogen-bonded networks that enhance crystallinity in thin films (Journal of Materials Chemistry C). In pharmaceutical research, the compound functions as a scaffold for developing photodynamic therapy agents. The anthracene chromophore absorbs light at therapeutic wavelengths (650-700 nm) and generates reactive oxygen species with quantum yields up to 0.45 for singlet oxygen production (Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology). In analytical chemistry, the compound acts as a fluorescent probe for detecting certain metal ions through photoinduced electron transfer mechanisms. Upon binding to specific transition metals, the fluorescence intensity increases by factors exceeding 100-fold with detection limits as low as 50 nM (Analytical Chemistry). In the field of supramolecular chemistry, the compound provides a platform for creating host-guest systems. The anthracene unit engages in - stacking interactions while the carboxylic acid group forms directional hydrogen bonds, enabling formation of 1:1 complexes with cyclodextrins with association constants up to 10^4 M^-1 (Chemistry - A European Journal).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review