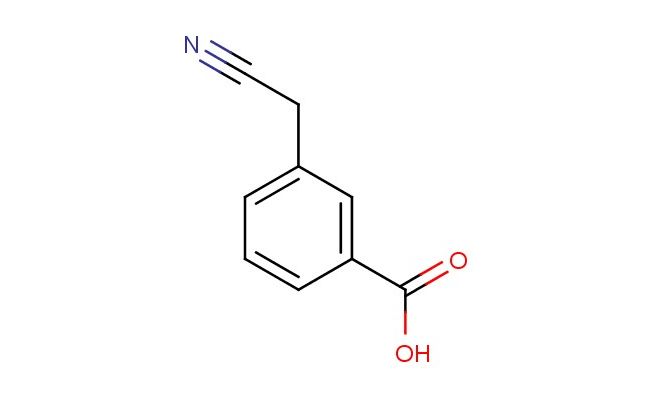
3-(cyanomethyl)benzoic acid
$250.00
CAS No.: 5689-33-8
Catalog No.: 196526
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H7NO2
MW: 161.16
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(#N)CC=1C=C(C(=O)O)C=CC1
Catalog No.: 196526
Purity: 95%
MF: C9H7NO2
MW: 161.16
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C(#N)CC=1C=C(C(=O)O)C=CC1
3-(cyanomethyl)benzoic acid; CAS No.: 5689-33-8; 3-(cyanomethyl)benzoic acid. PROPERTIES: 3-(cyanomethyl)benzoic acid is a white crystalline powder with a molecular formula of C9H7NO2. It has a molecular weight of 165.16 g/mol and a melting point of approximately 178-181 C. The compound exhibits moderate solubility in water and is more soluble in polar organic solvents like DMSO and DMF. It is sensitive to basic conditions and should be stored in a cool, dry place at temperatures below 25 C in a tightly sealed container. Safety precautions include avoiding skin contact and using gloves. It is classified as a category 3 skin irritant under GHS classification. APPLICATIONS: 3-(cyanomethyl)benzoic acid serves as a versatile intermediate in the synthesis of various nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), particularly those targeting cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) selectivity. Its cyano group provides essential electron-withdrawing effects for enzyme inhibition. In the field of materials science, this compound is used in the preparation of polymeric materials with enhanced thermal stability, as documented in Polymer Chemistry. It also functions as a building block for the synthesis of fluorescent probes for detecting biological thiols, where its carboxylic acid group facilitates conjugation to biomolecules. Additionally, the compound is employed in the development of novel electrochemical sensors for environmental monitoring applications, where its redox-active cyano group participates in electron transfer processes. Its unique electronic properties make it valuable in the synthesis of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for gas storage applications, as reported in the journal Chemical Materials, where its carboxylic acid group coordinates with metal centers to form porous structures.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review