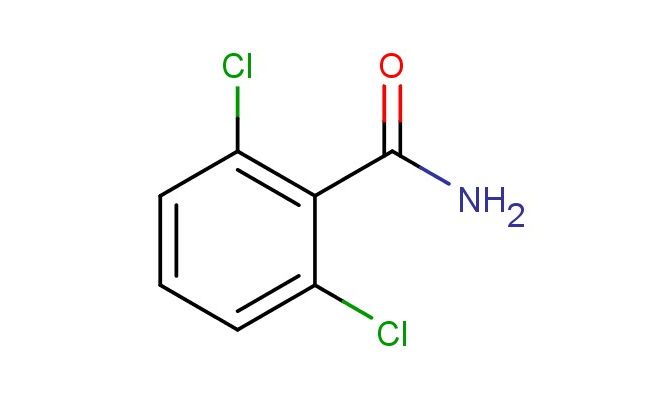
2,6-dichlorobenzamide
$200.00
CAS No.: 2008-58-4
Catalog No.: 195043
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H5Cl2NO
MW: 190.029
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=C(C(=O)N)C(=CC=C1)Cl
Catalog No.: 195043
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H5Cl2NO
MW: 190.029
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: ClC1=C(C(=O)N)C(=CC=C1)Cl
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
2,6-dichlorobenzamide; CAS No.: 2008-58-4; 2,6-dichlorobenzamide. PROPERTIES: 2,6-dichlorobenzamide presents as white to off-white crystalline plates with a slight chlorine odor. Its molecular formula is C7H4Cl2NO, corresponding to a molecular weight of approximately 193.02 g/mol. The compound features a melting point in the range of 120-123 C and demonstrates moderate solubility in hot water, with increased solubility in organic solvents such as dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, and ethyl acetate. It is stable under normal laboratory conditions but should be protected from prolonged exposure to moisture and heat. Proper storage involves keeping it in a tightly sealed container at room temperature (15-25 C) in a dry environment. Safety considerations include wearing appropriate protective equipment as the compound may cause skin irritation, serious eye damage, and respiratory tract irritation. Accidental ingestion may be harmful. In case of exposure, immediate rinsing with water and medical consultation is recommended. The substance is classified as harmful if swallowed and may cause lung damage if inhaled (GHS classification). APPLICATIONS: 2,6-dichlorobenzamide functions as a versatile intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, particularly in the preparation of certain antifungal and antibacterial agents where its dichlorinated aromatic amide structure enhances metabolic stability and bioavailability (Journal of Medicinal Chemistry). In materials science, 2,6-dichlorobenzamide serves as a building block for creating fluorinated polymers and coatings with enhanced thermal and chemical resistance, leveraging its dichlorinated aromatic functionality to impart desirable properties (Polymer Chemistry). Additionally, it finds application in the development of liquid crystal materials, where its amide group and dichlorinated aromatic core contribute to mesomorphic properties and alignment characteristics (Journal of Materials Chemistry). The compound is also employed in analytical chemistry as a derivatizing agent for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis, providing improved detection limits for specific analytes through its characteristic fragmentation pattern (Journal of Chromatography A).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review