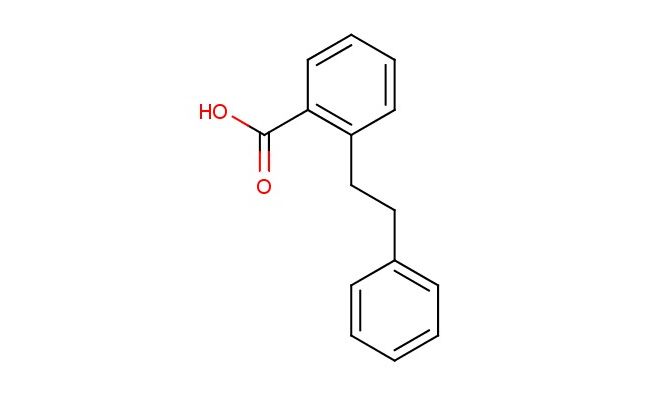
2-(2-phenylethyl)benzoic acid
$300.00
CAS No.: 4890-85-1
Catalog No.: 195047
Purity: 95%
MF: C15H14O2
MW: 226.275
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C1(=CC=CC=C1)CCC1=C(C(=O)O)C=CC=C1
Catalog No.: 195047
Purity: 95%
MF: C15H14O2
MW: 226.275
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: C1(=CC=CC=C1)CCC1=C(C(=O)O)C=CC=C1
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
2-(2-phenylethyl)benzoic acid; CAS No.: 4890-85-1; 2-(2-phenylethyl)benzoic acid. PROPERTIES: 2-(2-phenylethyl)benzoic acid presents as white to off-white crystalline powder with a slight aromatic odor. Its molecular formula is C14H12O2, corresponding to a molecular weight of approximately 208.25 g/mol. The compound features a melting point in the range of 125-128 C and demonstrates moderate solubility in hot water, with increased solubility in organic solvents such as methanol, ethyl acetate, and dimethylformamide. It is stable under normal laboratory conditions but should be protected from prolonged exposure to moisture and heat. Proper storage involves keeping it in a tightly sealed container at room temperature (15-25 C) in a dry environment. Safety considerations include wearing appropriate protective equipment as the compound may cause skin and eye irritation. Inhalation of dust should be avoided, and in case of accidental exposure, thorough washing with water and medical consultation is advised. APPLICATIONS: 2-(2-phenylethyl)benzoic acid functions as a versatile intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, particularly in the preparation of certain anti-inflammatory agents and analgesics where its phenylethyl substituent and carboxylic acid group provide structural features important for receptor binding and bioactivity (Journal of Medicinal Chemistry). In materials science, 2-(2-phenylethyl)benzoic acid serves as a building block for creating liquid crystal polymers and electro-optical materials, where its rigid aromatic structure and flexible ethyl linker enable desired mesomorphic properties and optical anisotropy (Journal of Polymer Science). Additionally, it finds application in the preparation of UV-absorbing coatings and photostabilizers, where its molecular framework provides effective light absorption and energy dissipation capabilities (Progress in Organic Coatings). The compound is also employed in organic synthesis as a starting material for the preparation of chiral building blocks through asymmetric transformations, enabling the synthesis of complex molecules with high stereochemical control (Tetrahedron Letters).
Reviews
Write Your Own Review