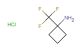
1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexanamine hydrochloride
$300.00
CAS No.: 1311315-20-4
Catalog No.: TQP3011
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H13ClF3N
MW: 203.635
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: Cl.FC(C1(CCCCC1)N)(F)F
Catalog No.: TQP3011
Purity: 95%
MF: C7H13ClF3N
MW: 203.635
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: Cl.FC(C1(CCCCC1)N)(F)F
For R&D use only. Not for human or animal use.
CAS NO.: 1311315-20-4; 1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexanamine hydrochloride. PROPERTIES: 1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexanamine hydrochloride appears as white crystalline solids with a characteristic ammoniacal odor. Its molecular formula is C7H13F3N HCl, corresponding to a molecular weight of 207.64 g/mol. The compound has a melting point between 185-189 C and is highly soluble in water, forming clear solutions. Proper storage requires maintenance at 2-8 degree Celsius in tightly sealed containers to prevent deliquescence. When handling, use corrosion-resistant equipment as it may cause corrosion to metals. The substance is a mild irritant and should be managed in well-ilatedvent areas to prevent inhalation of dust particles. It is stable under normal laboratory conditions but decomposes upon prolonged exposure to heat, releasing toxic fumes including hydrogen chloride. APPLICATIONS: 1-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexanamine hydrochloride functions as a chiral amine building block in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals with CNS activity. The trifluoromethyl group imparts unique metabolic stability, prolonging the half-life of resulting compounds. In medicinal chemistry, this compound serves as a starting material for developing antipsychotic agents where the cyclohexane ring system provides lipophilic character that enhances blood-brain barrier penetration. The hydrochloride salt form enhances water solubility, facilitating formulation development for parenteral administration. In materials science, derivatives of this compound are used to create chiral catalysts for asymmetric synthesis, where the cyclohexane framework induces stereoselectivity in carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions. Researchers in agrochemical development utilize this compound (though not for agricultural applications) to synthesize insecticides with novel modes of action, exploiting the trifluoromethyl group's ability to modulate receptor interactions. Additionally, the compound serves as a precursor for synthesizing musk odorants used in fine fragrance compositions, where the cyclohexane and trifluoromethyl groups contribute to the characteristic olfactory profile. The amine functionality allows for further derivatization, enabling the creation of odorants with varying diffusion rates and odor intensities for different application contexts.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review