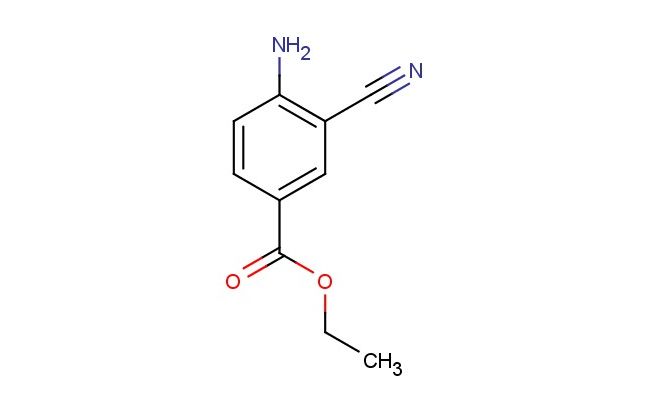
ethyl 4-amino-3-cyanobenzoate
$200.00
CAS No.: 1260742-52-6
Catalog No.: WLZ1793
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H10N2O2
MW: 190.202
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC1=C(C=C(C(=O)OCC)C=C1)C#N
Catalog No.: WLZ1793
Purity: 95%
MF: C10H10N2O2
MW: 190.202
Storage: 2-8 degree Celsius
SMILES: NC1=C(C=C(C(=O)OCC)C=C1)C#N
CAS NO.: 1260742-52-6; ethyl 4-amino-3-cyanobenzoate. PROPERTIES: This aromatic ester features a primary amine group and a cyano group on a benzene ring connected to an ethyl ester group, creating a molecule with potential applications in organic synthesis and pharmaceutical research. The ethyl 4-amino-3-cyanobenzoate typically appears as a white to off-white crystalline solid with moderate solubility in common organic solvents. Its molecular structure includes an electron-withdrawing cyano group and an electron-donating amine group that influence the electronic properties of the aromatic system. For optimal stability and to prevent degradation, this compound should be stored at 2-8 degree Celsius in a tightly sealed container under anhydrous conditions. When handling, appropriate safety measures including nitrile gloves and safety goggles are essential. This compound is sensitive to moisture and may hydrolyze in aqueous environments. In case of accidental spillage, clean the area with a damp cloth and dispose of materials according to local regulations. APPLICATIONS: The ethyl 4-amino-3-cyanobenzoate serves as a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of highly functionalized aromatic compounds and materials with specific electronic properties. The cyano group provides a handle for further functionalization through reactions such as reduction or hydrolysis. In medicinal chemistry, this compound functions as a building block for developing pharmaceuticals targeting enzyme inhibitors and receptor modulators. The ester group can be further modified for additional diversification. Additionally, the molecule finds utility in materials science as a monomer for creating polymers with specific electronic and optical properties. Researchers utilizing this compound benefit from its defined substitution pattern, enabling the development of advanced materials with tailored electronic characteristics.
Reviews
Write Your Own Review